Sanitation is the management and disposal of different types of wastes including human waste, to minimise harmful effects to human health and the environment.
The full cycle of sanitation (FCS) includes five stages, namely,
1) safe containment (consisting of toilets and septic tanks/drainage systems),
2) safe emptying services like de-sludging,
3) safe transport of waste by trucks,
4) safe treatment in sewage treatment plants / fecal sludge treatment plants and
5) safe disposal/reuse. The stages are explained in the diagram below.
Containment in full cycle of sanitation is the stage where the human waste is collected through toilets and stored in a containment structure like a septic tank or a twin pit.
Toilets are physical structures/buildings where human beings defecate. Toilets are of three types:
1) Individual Household Toilets,
2) Community Toilets and
3) Public Toilets.
Toilets that are with the premises of an individual house and are used by the people living in that house are called individual household toilets.

Toilets that are situated in a common place where certain number of families living within a community can use are called community toilets.

Figure 3: Community Toilet
Source: (Indian Institute for Human Settlements, 2017)
Toilets that are available in public places like bus stand, railway station, or parks are called public toilets.

Figure 4: Public Toilet
Source: (Indian Institute for Human Settlements, 2017)
Toilets are classified depending on their sanitary status. 1) Sanitary Toilet, and 2) Insanitary Toilet.
A sanitary toilet is a toilet which is connected to a septic tank or a twin pit because of which the waste does not leak into the environment.
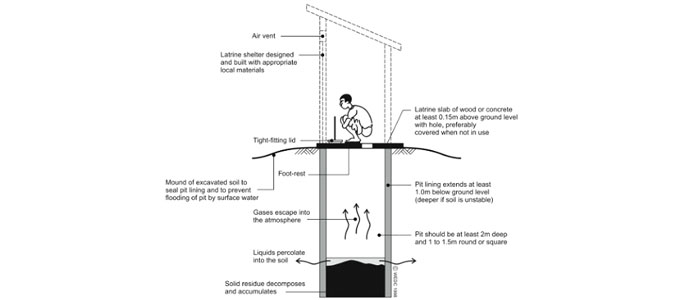
An insanitary toilet is a toilet (such as pit latrines) where the human waste leaks into the environment as the toilet is not connected to any safe containment structures like septic tank or twin pit.
A septic tank is a rectangular structure placed underground to collect and store human waste coming from the toilets from which it is periodically emptied. The outlet of a septic tank is connected to a soak pit.
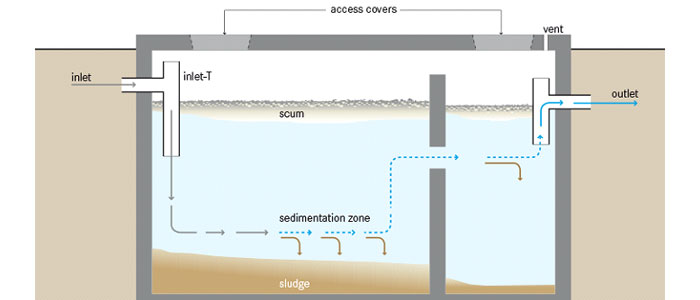
A soak pit is also a containment structure where the partially treated human waste from septic tank is collected and stored.

Septic Tank is a type of on-site system which is connected to the toilet, into which the fecal matter flows after being flushed. An ideal septic tank should have a minimum width of 750 mm and liquid depth of 1 m. The length should be 2 to 4 times the width. The dimensions of septic tank vary with the number of users. (Suitable sizes of septic tank are given in in the Operative Guidelines for Septage Management for Local Bodies in Tamil Nadu, 2014)
A twin-pit is a containment structure that has two cylindrical pits connected to each other through a pipe. When one pit gets filled with human waste from toilets, then the connection to the filled pit is closed, and the toilet pipe is connected to the second pit to collect the human waste. The distance between two pits should be at least 1 meter. By the time the second pit is filled, the partially treated human waste from the first pit is emptied, and made available for collection of human waste.

Figure 8: Twin-pit
Source: (Sulabh International Social Service Organisation, 2015)
Places where underground sewage systems are not possible, containment structures like septic tank or twin-pit are used to collect the human waste. Since these containment structures are located near to the toilets, these are called on-site sanitation systems.
Fecal Sludge (FS) (also called septage) is the material that is collected from pit latrines, septic tanks or other onsite sanitation facilities (OSSF) and not transported through a sewer. Fecal Sludge is raw or partially digested, slurry or semisolid in nature.
Septage management or Fecal Sludge Management (FSM) includes the storage, collection, transport, treatment and safe end-use or disposal of fecal sludge. The sustainable implementation of septage management requires an integrated approach which incorporates technology, management and planning.
Emptying (or) de-sludging is a process, where the septage is emptied from the septic tank by de-sludging operators using suction pipes in situations of septic tank overflowing or cleaning purposes.

Figure 9: Emptying/De-sludging
Source: (Indian Institute for Human Settlements, 2017)
Transport is the third stage of FCS, where the de-sludging trucks carry the desluged septage, and discharge it directly into the sewage or fecal sludge treatment plant., or into decanting facilities of the sewage treatment plants.

Figure 10: Transport of Septage
Source: (Indian Institute for Human Settlements, 2017)
Desludging Vehicle is a vehicle with a suction tanker mounted on the Truck/Tractor etc. The tanker is fitted with a motor which sucks the sludge/septage from the on-site systems. The capacity of the tanker usually varies from 4000 to 8000 liters.
Decanting facility is a point where septage from on-site sanitation systems like pit latrines and septic tank is pumped into the underground sewerage systems, to be treated at the centralized treatment plant. These assigned stations for emptying the septage are called decanting stations.

Figure 11: Decanting
Source: (Indian Institute for Human Settlements, 2017)
The fourth stage in FCS is treatment, where the septage transported and discharged by trucks or through decanting facilities undergoes treatment, thereby making it safe for reuse.

Figure 12: Treatment Facility
Source: (Indian Institute for Human Settlements, 2016)
A Fecal Sludge Treatment Plant (FSTP) is a treatment facility where the septage transported through de-sludging trucks is treated to make it environmentally safe for disposal or reuse.
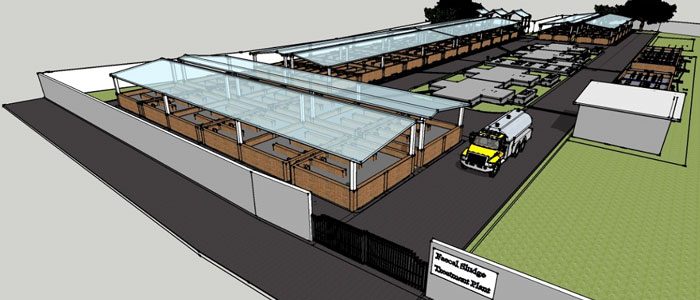
Figure 13: Fecal Sludge Treatment Plant (FSTP) – Top View Layout
Source: (Indian Institute for Human Settlements, 2017)
Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) is a treatment facility where the human waste collected and carried through underground drainage systems is treated to make it environmentally safe for disposal or reuse.

Figure 14: Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) – Top View
Source: (Indian Institute for Human Settlements, 2016)
Disposal/Reuse is the final stage of the FCS. In this stage, the treated human waste is either disposed of safely into the environment or can be reused as farm manure or biofuel. The treated water which is separated from septage can be used for gardening, cooling purposes in industries, etc.
IIHS Chennai
Floor 7A, Chaitanya Exotica,
24/51 Venkatnarayana Road,
T Nagar, Chennai 600 017. India
P: +91 44 6630 5500/6555 6590
IIHS
D-59, 6th Cross,
Thillainagar,
Trichy – 620018.
Ph: 0431-4972130 / 4973130